PUBLISHED
RESEARCH
FEMALES HAVE LOWER KNEE STRENTGH AND VERTICAL GROUND REACTION FORCES DURING LANDING THAN MALES FOLLOWING ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION AT THE TIME OF RETURN TO SPIRIT
There is a high rate of second anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury (ipsilateral graft or contralateral ACL) upon return-to-sport (RTS) following ACL reconstruction (ACLR). While a significant amount of epidemiological data exists demonstrating sex differences as risk factors for primary ACL injury, less is known about sex differences as potential risk factors for second ACL injury. The purpose of this study is to determine if there are sex-specific differences in potential risk factors for second ACL injury at the time of clearance for RTS.
A RADIOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF PROXIMAL HUMERAL ANATOMY IN PATIENTS WITH PRIMARY GLENOHUMERAL ARTHRITIS…
While short stems in total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) preserve bone stock and facilitate revision surgery, they have been associated with higher rates of malalignment and loosening in some cases compared to standard length stems. The purpose of this study was to analyze the intramedullary canal in progressive increments distal to the greater tuberosity to provide anatomic information about the optimal length of press-fit short stems for alignment and stability in TSA.
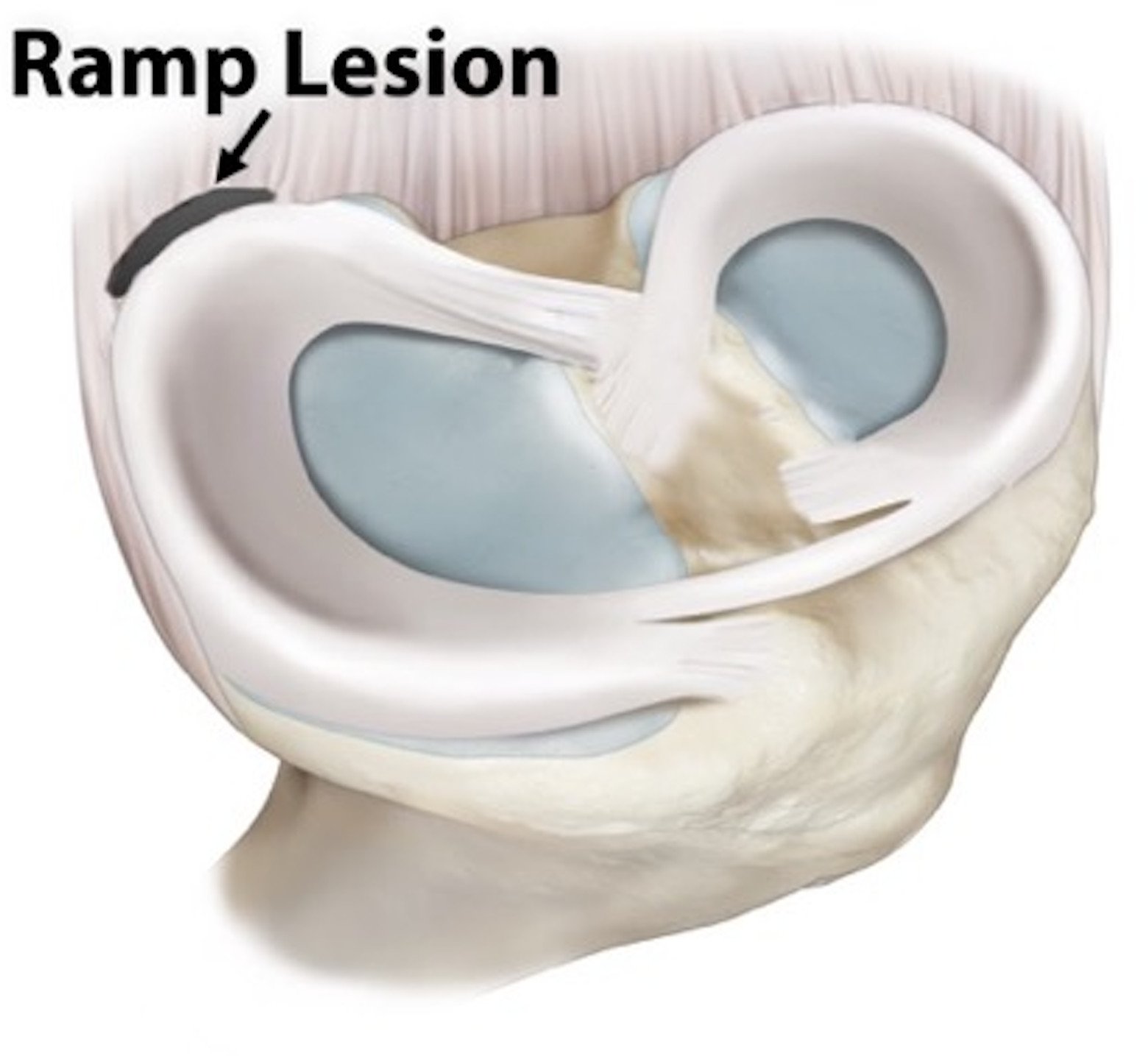
MENISCAL RAMP LESIONS - SKILLFUL NEGLECT OR ROUTINE REPAIR?
Meniscal ramp lesions are injuries of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus at the meniscocapsular junction or the meniscotibial ligament and are frequently associated with concomitant anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury.
Our objective is to review the current literature on meniscal ramp lesion management to better define the indications for and outcomes of repair.
ARTHROSCOPIC ALL-INSIDE REPAIR OF MENISCAL RAMP LESIONS
Meniscal ramp lesions are disruptions of the posterior meniscotibial attachment of the medial meniscus and are commonly associated with anterior cruciate ligament injuries. However, they can be frequently missed when reviewing standard magnetic resonance imaging and difficult to treat. In this presentation, we describe our approach to repair a meniscal ramp lesion using a minimally invasive all-inside technique.
ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION DISPLAYS FAVORABLE OUTCOMES: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
To systematically review the literature to determine the injury mechanisms, presentation, and timing of diagnosis for pediatric patients with intratendinous rotator cuff tears and to determine the efficacy of surgical intervention for affected patients.
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING FINDINGS OF THE ASYMPTOMATIC SHOULDER MAY IMPACT PERFORMANCE, NOT FUTURE INJURY LIST PLACEMENT IN MAJOR LEAGUE BASEBALL PITCHERS
Three blinded reviewers reviewed all MRI scans independently to evaluate for the presence of abnormalities in the rotator cuff (RTC), labrum, capsule, long-head of the biceps tendon (LHBT), and humeral head. Binary imaging findings were correlated to future placement on the IL for subsequent shoulder complaints. Bivariate statistics using Student’s t-tests and Fisher exact tests (both α = .05) were used in this study
THE MINIMAL CLINICALLY IMPORTANT DIFFERENCE, SUBSTANTIAL CLINICAL BENEFIT, AND PATIENT-ACCEPTABLE SYMPTOMATIC STATE AFTER MEDIAL PATELLOFEMORAL LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION
This retrospective cohort study used a prospectively maintained database of patients undergoing primary MPFLR between August 2015 and December 2019. PROMs included the International Knee Documentation Committee (IKDC), Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS), KOOS joint replacement (JR), and Kujala. Anchor-based and distribution-based methods were used to calculate the MCID, SCB, and PASS. Regression analyses were performed to identify prognosticators for achievement of clinically significant thresholds.
THE QUALITY AND ACCURACY OF DIRECT-TO-CONSUMER BIOLOGIC MARKETING FOR SHOULDER PATHOLOGY ARE POOR
Eight search terms relevant to shoulder biologic therapies (shoulder + BMAC, Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate, PRP, Platelet Rich Plasma, Lipogems, Adipose Tissue, Biologic therapy, and Stem cell therapy) were searched across three separate search engines. The first 25 websites of each search were recorded. Duplicate websites and those not specific to shoulder pathology were excluded. Three evaluators independently assessed quality using an author-derived scoring rubric for a total of 25 possible points and accuracy for a total of 12 possible points. The Flesch-Kincaid readability test was used to quantify reading levels. Websites were further characterized by authorship and the presence of commercial bias.
OUTCOMES AND COMPLICATIONS OF DISTAL HUMERAL HEMIARTHROPLASTY FOR DISTAL HUMERAL FRACTURES - A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Distal humeral hemiarthroplasty has been performed for a variety of indications with the most common being management of distal humeral fractures. This systematic review evaluates the outcomes and complications of distal humeral hemiarthroplasty for this pathology.
A PILOT MULTICENTER RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL COMPARING BANKART REPAIR AND REMPLISSAGE WITH THE LATARJET PROCEDURE IN PATIENTS WITH SUBCRITICAL BONE LOSS (STABLE):STUDY PROTOCOL
Anterior dislocations, the most common type of shoulder dislocation, are often complicated by subsequent instability. With recurrent dislocations there often is attrition of the labrum and progressive loss of the anterior bony contour of the glenoid. Treatment options for this pathology involve either soft tissue repair or bony augmentation procedure. The optimal management remains unknown and current clinical practice is highly varied.
RETURN TO SPORT FOLLOWING DISTAL TRICEPS REPAIR
Patients who underwent distal triceps repair with a minimum of 1 year of follow-up were retrospectively reviewed. Patients completed a subjective sports questionnaire and were scored on a visual analog scale for pain; the Mayo Elbow Performance Index; the Quick Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand; and the Single Assessment Numerical Evaluation.
PREOPERATIVE FACCTORS ASSOCIATED WITH PRESS GANEY PATIENT SATISFACTION SCORES AFTER ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION
Patients undergoing primary or revision ACLR at a single urban center between June 2015 and August 2019 were identified retrospectively under approval of the institutional review board. At our institution, all adult patients (≥18 years) received the PG Ambulatory Surgery (PGAS) survey within 48 hours to 6 weeks postoperatively by mail or e-mail. During the study period, nine surgeons performed 829 ACLR procedures and a total of 99 patients completed the PGAS survey (11.9%).
NOOPERATIVE AND OPERATIVE SOFT-TISSUE, CARTILAGE, AND BONY REGENERATION AND ORTHOPAEDIC BIOLOGICS OF THE SHOULDER…
Various orthopaedic biologics (orthobiologics) have been investigated for the treatment of pathology involving the shoulder including the rotator cuff tendons, glenohumeral articular cartilage, glenoid labrum, the joint capsule, and bone.
ASPERITY LEVEL CHARACTERIZATION OF ABRASIVE WEAR USING ATOMIC FORCE MICROSCOPY
Using an atomic force microscope, a nanoscale wear characterization method has been applied to a commercial steel substrate AISI 52100, a common bearing material. Two wear mechanisms were observed by the presented method: atom attrition and elastoplastic ploughing. It is shown that not only friction can be used to classify the difference between these two mechanisms, but also the ‘degree of wear’. Archard's Law of adhesion shows good conformity to experimental data at the nanoscale for the elastoplastic ploughing mechanism. However, there is a distinct discontinuity between the two identified mechanisms of wear and their relation to the load and the removed volume. The length-scale effect of the material's hardness property plays an integral role in the relationship between the ‘degree of wear’ and load. The transition between wear mechanisms is hardness-dependent, as below a load threshold limited plastic deformation in the form of pile up is exhibited. It is revealed that the presented method can be used as a rapid wear characterization technique, but additional work is necessary to project individual asperity interaction observations to macroscale contacts.
ACROMIOCLAVICULAR JOINT INJURIES: EFFECTIVE REHABILITATION
Studies were identified by searching the MEDLINE database from 01/1995 to 09/2020. Included studies contained detailed rehabilitation protocols with physiologic rationale for AC joint injuries. Biomechanical studies, technique articles, radiographic studies, systematic reviews, case studies, editorials, and studies that compared nonoperative versus operative treatment without focus on rehabilitation were excluded. Following identification of the literature, an updated treatment algorithm was created.
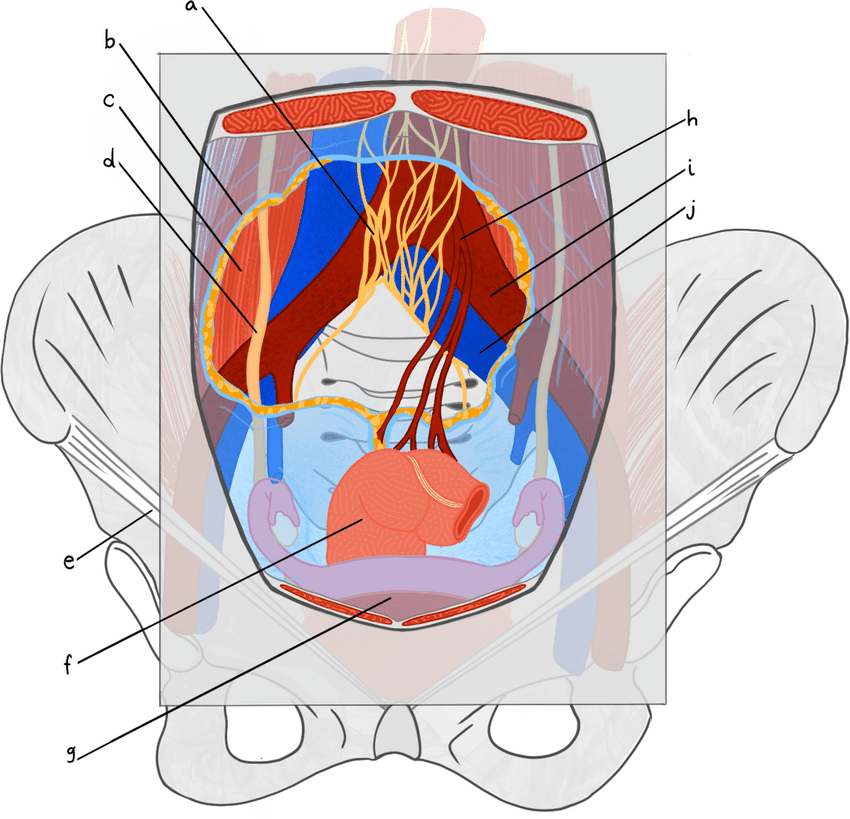
GENITOURINARY COMPLICATIONS IN ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY
Genitourinary complications following orthopaedic intervention are uncommon but well-described occurrences and exist on a spectrum of severity. These complications vary depending on the anatomic location and surgical approach, with surgery of the spine, hip, and pelvis of particular concern. Injuries to the urinary tract may present acutely with urinary retention or hematuria. However, they often have a delayed presentation with severe complications such as urinary fistula and recurrent infection. Delayed presentations may place the onus of timely and proper diagnosis on the orthopaedic provider, who may serve as the patient’s primary source of long-term follow-up. Detailed knowledge of anatomy and at-risk structures is key to both preventing and identifying injury. Although iatrogenic injury is not always avoidable, early identification can help to facilitate timely evaluation and management to prevent long-term complications such as bladder dysfunction, obstructive renal injury, sexual dysfunction, and chronic pain.
RISK FACTORS FOR POSTOPERATIVE BLOOD TRANSFUSION AFTER SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY
Shoulder arthroplasties for osteoarthritis (OA) (N = 47), rotator cuff arthropathy (RCA) (N = 50), fracture (N = 76), revision (N = 66), and periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) (N = 35) performed at a single institution during a 6-year period were included. All other indications were excluded. Patient-based and surgical risk factors, including surgical indication, for postoperative allogeneic red blood cell transfusion were assessed with multivariate logistic regression analysis.